Does a steering rack and tie rod need to be aligned after replacing it?
In car maintenance, replacing steering system components is a common operation, especially the steering rack and tie rod. Whether due to wear, aging, or other factors, these key components play a vital role in the driving process of the car. Therefore, when replacing these parts, many car owners and maintenance technicians will face an important question: "Do I need to align the steering rack and tie rod after replacing it?" The answer is yes, in other words, after replacing these parts, the geometric relationship between the vehicle's tires, suspension system and steering system must be recalibrated to ensure the safety, stability and driving experience of the vehicle.
This article will explore in depth why a four-wheel alignment (or "alignment") must be performed after replacing the steering rack and tie rod, the specific role of the four-wheel alignment, and the possible consequences of ignoring this step. By analyzing these aspects, car owners and maintenance technicians can better understand the importance of this operation and ensure that the vehicle is in the best condition after the repair.
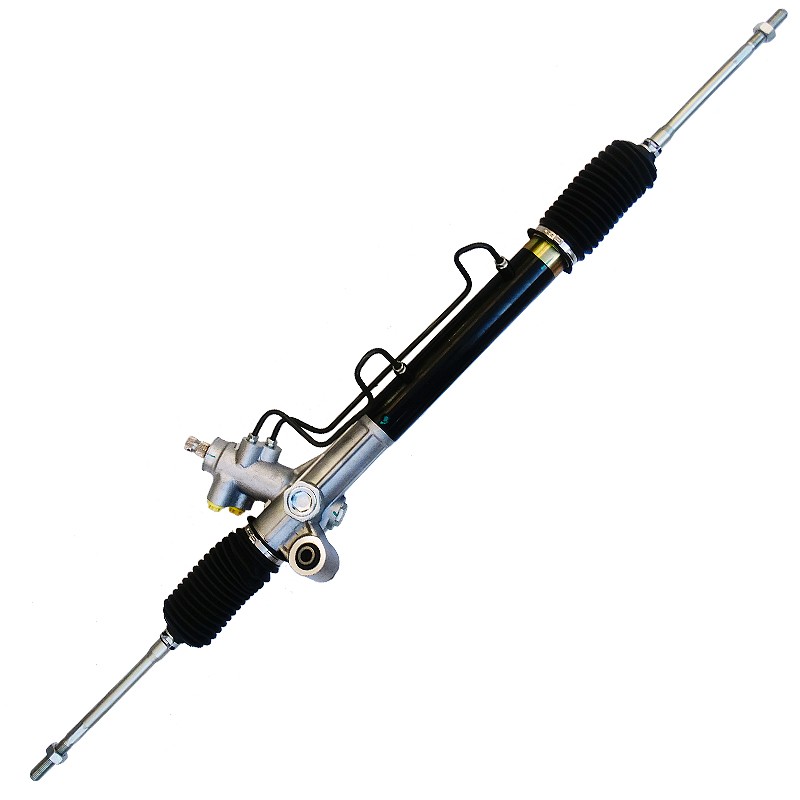

What is a steering rack and tie rod?
Before understanding why alignment is required after replacing these parts, it is first necessary to clarify what the steering rack and tie rod are and their role in the vehicle.
Steering rack
The steering rack (or rack-type steering gear) is one of the core components of the vehicle's steering system. Its main function is to transmit the driver's steering wheel movement to the wheels through gears to achieve the steering of the vehicle. The steering rack is usually connected to the steering wheel through the steering column. When the steering wheel turns, the rack changes the direction of the wheels through the mechanical transmission of the gears, thereby achieving the steering operation of the vehicle.
Tie rod
The tie rod is an important component connecting the steering rack and the wheel knuckle. Tie rods usually come in two types: inner tie rods and outer tie rods. The inner tie rod connects the steering rack, and the outer tie rod connects the steering knuckle. Together, they form part of the steering system. Through the synergy of the inner and outer tie rods, the steering force is transmitted from the rack to the wheel, ultimately achieving left and right rotation of the wheel.
The length and connection method of the tie rod directly affect the angle and steering angle of the wheel, and even small differences in these angles can have a significant impact on the vehicle's driving stability and tire wear.
What effect does replacing the steering rack and tie rod have on the vehicle geometry?
The steering rack and tie rod are key geometric components of the vehicle. They are closely related to the wheels and suspension system, and directly affect the vehicle's toe angle, wheel alignment, and vehicle handling stability. Replacing these components means that the geometric relationship of the wheels has changed, so it is necessary to perform a four-wheel alignment calibration to restore the vehicle to normal driving conditions.
Effect of toe angle
The toe angle refers to the geometric relationship between the front wheels of the vehicle, specifically the difference between the distance between the leading edge of the wheel and the distance between the trailing edge. When the distance between the leading edge of the wheel is smaller than the trailing edge, it is called "toe-in"; otherwise, it is "toe-in". The toe angle is crucial to the straight-line driving stability of the vehicle. It affects the way the wheel contacts the ground, which affects the steering response of the vehicle and the wear of the tires.
When replacing the steering rack and tie rod, any slight installation deviation will affect the toe angle, causing the wheel to deviate to one side when the vehicle is driving, inaccurate steering, and even accelerated abnormal wear of the tires. Therefore, the toe angle must be readjusted after replacing these components to ensure that the vehicle can drive in a straight line and avoid unnecessary tire wear.
Effect of wheel alignment
Wheel alignment refers to the geometric relationship between the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, which directly affects the balance, handling and tire wear of the vehicle when turning. The adjustment of the steering rack and tie rod has a direct impact on the wheel alignment, because the size and installation position of these components determine the steering angle and inclination of the wheel.
If the wheel alignment is not accurate, it may cause the vehicle to deviate from the straight line while driving, or even over- or under-steer when turning. To avoid this, the wheel alignment must be calibrated after replacing these steering components.
Effect of steering angle
The length and installation position of the steering rack and tie rod directly determine the steering angle of the wheel. When replacing these components, a small error in the steering angle may cause the vehicle to be unresponsive when turning or unstable on a curve. If the steering angle is not adjusted accurately, the handling performance of the vehicle while driving will be negatively affected, increasing the difficulty and risk of driving.

Why is alignment necessary after replacing the steering rack and tie rod?
After replacing the steering rack and tie rod, the geometric parameters of the vehicle have changed. Since the steering system and suspension system are closely connected, these changes not only affect the steering accuracy, but may also cause problems such as increased tire wear, unstable steering, and poor driving experience. Four-wheel alignment (i.e. alignment) is the process of accurately adjusting the geometric parameters of the wheels to return them to the original factory settings or close to the ideal state. The following are several main reasons why four-wheel alignment is necessary.
Ensure driving safety
After replacing the steering rack and tie rod, the vehicle's handling may change significantly, especially when driving at high speeds or making sharp turns. If the parameters such as the toe angle and tilt angle of the wheel are not calibrated, the vehicle is prone to oversteering or understeering in these situations, increasing the risk of loss of control. Therefore, timely four-wheel alignment can ensure that the geometric relationship between the steering system and the suspension system meets safety standards and reduce the possibility of accidents.
Prevent abnormal tire wear
Incorrect wheel alignment can cause uneven wear of the tires and even greatly shorten the service life of the tires. For example, if the toe angle is inaccurate, the inner or outer side of the tire may be under too much pressure when the vehicle is driving in a straight line, resulting in asymmetric wear. Excessively worn tires not only reduce driving comfort, but also increase the risk of tire blowouts. Four-wheel alignment ensures that the tires are evenly stressed during driving, thereby extending tire life.
Improve driving experience
Accurate four-wheel alignment can significantly improve the driving experience. When the wheel geometry parameters are precisely adjusted, the stability and responsiveness of the vehicle while driving will be improved. The steering wheel feedback is more sensitive and the steering is more precise, thereby improving driving safety and comfort. For car owners, a better driving experience not only increases driving pleasure, but also reduces fatigue from long-term driving.
Maintain the stability of vehicle performance
The design of the car has undergone complex calculations and experiments to ensure its stability and handling under various road conditions. After replacing the steering rack and tie rods, if the wheel alignment adjustment is not performed, the performance of the vehicle may deviate, affecting its performance on different road surfaces. Four-wheel alignment can restore the vehicle to a state close to the original design, thereby maintaining the stability of its overall performance.
What are the basic steps of four-wheel alignment?
Performing a four-wheel alignment after replacing the steering rack and tie rods is a technically demanding operation. It requires not only precise equipment, but also experienced technicians to measure and adjust the vehicle. The following are the general steps for four-wheel alignment:
Preliminary inspection
First, the technician will conduct a preliminary inspection of the vehicle to confirm that the replaced parts have been installed correctly and that other parts (such as the suspension system, wheels, etc.) are not damaged or worn. At this time, the tire pressure will also be checked to see if it is normal, because incorrect air pressure will affect the accuracy of the four-wheel alignment.
Measure the current geometric parameters
Using a dedicated four-wheel alignment instrument, the technician will measure the toe angle, camber angle and other geometric parameters of the current wheel. These data will be compared with the original parameters of the vehicle to determine the range and items that need to be adjusted.
Adjust the steering system and suspension system
Based on the measurement results, the technician will gradually adjust the geometric parameters of the wheel to the ideal state by adjusting the tie rod, the eccentric bolts of the suspension system, etc. Usually, the technician will start with the front wheel and then adjust the rear wheel as needed.
Remeasure and calibrate
After completing the adjustment, the technician will use the instrument to measure the geometric parameters of the wheel again to ensure that all values are within the specified range. If some parameters still do not meet the requirements, further fine-tuning is required until all data meet the standards.
Final inspection and testing
After completing the four-wheel alignment, the technician will also conduct a final inspection of the entire steering system and suspension system, and conduct a road test to ensure that the vehicle's handling and stability return to normal.

What are the consequences of ignoring four-wheel alignment?
Although four-wheel alignment is a vital operation, some car owners or maintenance technicians may ignore this process due to time or cost reasons. However, such an approach may bring a series of negative consequences:
1. Poor driving stability: If the geometric parameters of the wheels are not adjusted in place, the vehicle may have problems such as deviation and steering failure when driving at high speeds, increasing the danger of driving.
2. Rapid tire wear: Vehicles that have not undergone four-wheel alignment often have uneven tire wear, which not only shortens the tire life, but also may cause increased vibration when the vehicle is driving, affecting driving comfort.
3. Increased vehicle energy consumption: Improper wheel alignment may increase the resistance of the vehicle when driving, thereby increasing fuel consumption and increasing the cost of using the vehicle.
If you're looking for reliable and cost-effective power steering systems, DKM is the supplier you can trust. Established in 1996, we offer gear rack steering systems for a range of vehicle brands, from Toyota to Hyundai. Our advanced factory setup ensures efficient production and delivery for bulk orders. With a focus on wholesale pricing and customized manufacturing, DKM caters to global distributors and OEMs. Contact us now to learn more about our low-cost solutions and take advantage of our promotional offers on large purchases.




