How does power steering affect rack and pinion?
In modern cars, the performance and reliability of the steering system directly affect driving safety and handling. As one of the core components of the steering system, the rack and pinion bear the key task of converting the driver's steering operation into tire rotation. With the introduction of power steering technology, the working methods and load conditions of the rack and pinion have changed significantly.
So, how does power steering affect the rack and pinion? In addition, what components does a car's steering system consist of, and what are their respective functions?

What are the basic principles of power steering?
To understand how power steering affects the rack and pinion, you first need to understand the basic principles of a power steering system. The main function of the power steering system is to provide additional power assistance so that the driver does not need to exert too much force when turning the steering wheel, thereby improving driving comfort and vehicle controllability.
The working mechanism of power steering:
1. Hydraulic power steering: The hydraulic power steering system pressurizes hydraulic oil through a hydraulic pump and delivers it to the power cylinder in the steering rack. When the driver turns the steering wheel, hydraulic oil moves the piston, providing power assistance and making steering easier.
2. Electric power steering: The electric power steering system provides assistance through an electric motor. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the sensor detects the rotation angle and torque of the steering wheel. The electronic control unit (ECU) controls the operation of the electric motor based on the sensor data to assist the driver in completing the steering operation.
Regardless of the type of power steering system, their core purpose is to reduce the driver's operating burden through additional power assistance. It is precisely because of the introduction of this power assist that the working conditions of the rack and pinion have been significantly optimized.
How does power steering affect rack and pinion?
The rack and pinion are the core mechanical components of the steering system. They are directly responsible for converting the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the steering motion of the wheels. In a traditional mechanical steering system, the rack and pinion need to withstand all the torque exerted by the driver, which means that they will bear a large mechanical load during the steering process. However, the introduction of power steering changed this significantly.
1. Reduce mechanical load:
In a traditional manual steering system, the rack and pinion need to withstand the torque directly exerted by the driver. This direct mechanical effect often leads to increased wear of the rack and pinion, especially when frequent steering or low-speed steering is required. .
The power steering system greatly reduces the mechanical load on the rack and pinion by providing additional power assistance. In the hydraulic power steering system, the hydraulic assist provided by the hydraulic pump shares the force exerted by the driver, so that the rack and pinion are more evenly stressed during steering and reduce the rate of wear. Likewise, the electric motor assist in the electric power steering system plays a similar role.
2. Improve the responsiveness of the steering system:
The power steering system not only reduces the mechanical load, but also improves the responsiveness of the steering system. Without power steering, the driver needs to apply greater force to turn the steering wheel, which can cause delays in steering operations. However, with power steering's assist, steering operations become easier and quicker, meaning the rack and pinion respond more quickly to the driver's commands, improving the overall driving experience.
3. Improve vehicle handling:
The power-assisted nature of the power steering system allows the rack and pinion to maintain good handling over a wider speed range. When driving at low speeds, the power steering system provides high assist so that the driver can steer easily, while when driving at high speeds, the assist will be appropriately reduced to ensure steering accuracy. This variable assist feature not only improves vehicle handling, but also extends the life of the rack and pinion.
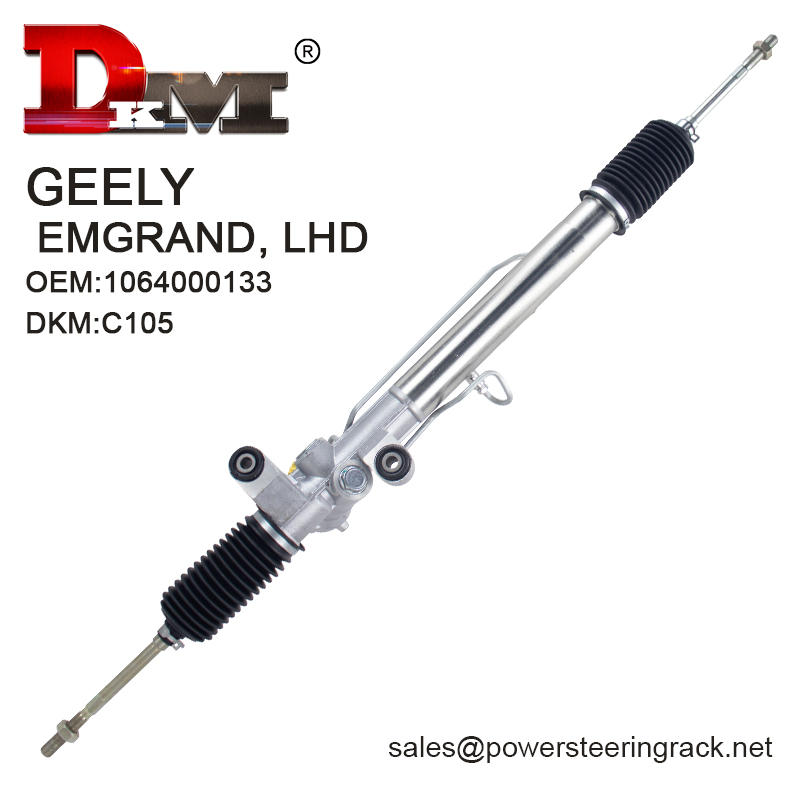

What components does a car's steering system consist of?
After understanding the impact of power steering on the rack and pinion, let's take a look at the overall structure of the car's steering system. The steering system is composed of multiple components, and their respective functions complement each other to ensure the vehicle's steering performance under different driving conditions.
1. Steering wheel:
The steering wheel is the direct interface between the driver and the steering system. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering shaft transmits this rotational motion to the steering gearbox, thus starting the entire steering process.
2. Steering column and steering shaft:
The steering column (or steering shaft) connects the steering wheel and the steering gear box and is responsible for transmitting the rotational motion of the steering wheel to the gear box. The steering column in modern cars is usually designed with a certain anti-collision function to absorb impact and protect the driver in the event of a collision.
3. Steering gearbox (gear and rack):
The steering gearbox is the core component of the entire steering system. It consists of pinion and rack. When the steering shaft transmits the rotational motion of the steering wheel to the pinion gear, the pinion gear slides along the rack, thereby converting the rotational motion into lateral linear motion, thereby pushing the front wheels to turn.
4. Tie rods (cross tie rods and straight tie rods):
The tie rod is an important component that connects the steering rack to the wheels. The tie rod (or tie rod assembly) transmits the lateral movement of the rack to the straight tie rod, which is then connected to the steering knuckle arm and ultimately transmits this motion to the wheels. Through a tie rod system, the movement of the rack is converted into the steering angle of the wheels.
5. Steering knuckle and hub:
The steering knuckle is a key component that connects the tie rod and the wheel. It controls the steering angle of the wheel through the steering shaft and hub. The structural design of the steering knuckle plays an important role in the responsiveness of the steering system and the steering angle of the wheels.
6. Power steering pump and power cylinder (hydraulic power steering system):
In the hydraulic power steering system, the power steering pump is responsible for providing hydraulic pressure to the entire system, and the power cylinder is responsible for converting the hydraulic pressure into mechanical motion to assist the steering rack to complete the steering operation.
7. Motor and sensors (electric power steering system):
In the electric power steering system, the electric motor replaces the function of the hydraulic pump and provides power to the steering rack. The sensor is responsible for detecting the rotation angle and torque of the steering wheel and transmitting the data to the electronic control unit (ECU) to control the operation of the electric motor.
8. Electronic control unit (ECU):
The electronic control unit is the "brain" of the electric power steering system. It adjusts the operation of the electric motor in real time based on sensor data to provide optimal steering assistance. This intelligent control system enables the vehicle to maintain good steering performance under different driving conditions.
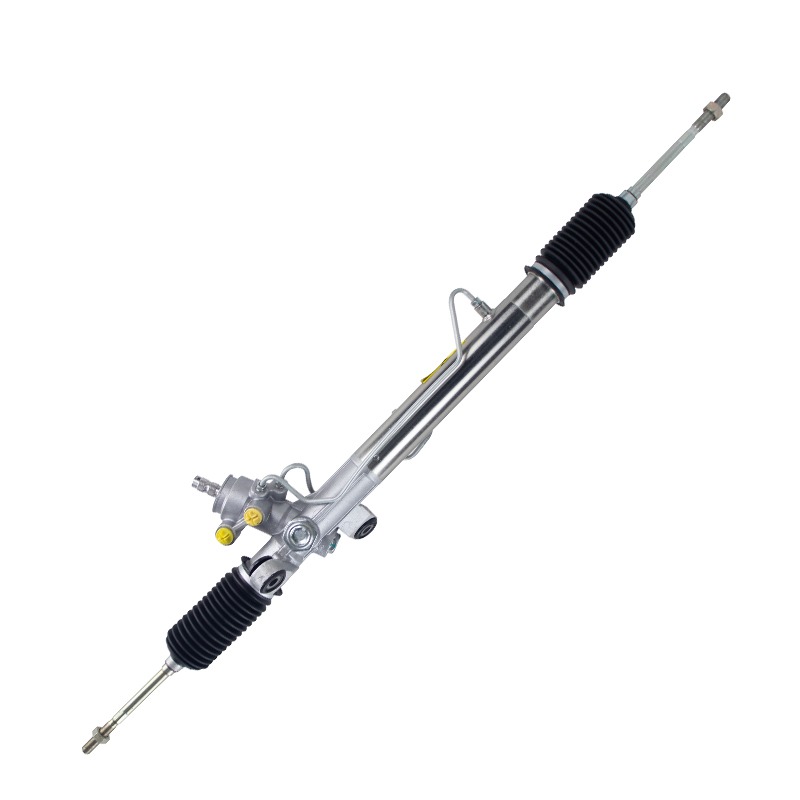

Overall cooperation of the steering system
The various components of a car's steering system work closely together to ensure the vehicle's steering safety and comfort under various driving conditions. Through the steering wheel and steering column, the driver's operation is transmitted to the steering gearbox, where the rack and pinion convert this operation into steering movement of the wheels. With the help of the power steering system, the load on the rack and pinion is reduced, and the working efficiency and response speed of the entire system are improved.
In addition, whether it is a hydraulic power steering system or an electric power steering system, their power assistance greatly improves the convenience of driving. Especially during long-term driving or complex road conditions, the power steering system's power-assisted characteristics can effectively reduce driving fatigue and improve driving safety.




