Manual Steering System Vs. Power Steering System: What's the Difference?
In the development of the automotive industry, the steering system has evolved from simple mechanical operation to today's highly intelligent and automated. Manual steering system and power steering system are two important milestones in this development process. Although most modern cars use power steering systems, manual steering systems are still representative. For car owners and enthusiasts who don't know much about the difference between the two, it is important to understand the differences between the two systems.
This article will explore the differences between manual steering system and power steering system from multiple perspectives such as design principles, operating experience, maintenance costs, and vehicle handling.

Basic Concepts of Manual Steering System and Power Steering System
To discuss the difference between manual steering system and power steering system, you first need to understand the basic concepts and working principles of these two systems.
What is a manual steering system?
Manual steering system, also known as mechanical steering system, is the earliest automotive steering technology. It transmits the rotational motion of the steering wheel to the wheels of the vehicle through a physical connection. The core components of a manual steering system include a steering wheel, a steering column, a steering gear (such as a rack and pinion mechanism or a worm gear mechanism), and a connecting rod. These components work together to directly convert the driver's steering action into the steering angle of the wheel.
The operation of the manual steering system is completely dependent on the driver's strength, without external power assistance, so a large steering force is required at low speed or when parking. Despite this, the manual steering system was widely used in early cars due to its simple structure, low maintenance cost and high reliability.
What is a power steering system?
The power steering system is developed on the basis of the manual steering system. It assists the driver's steering operation by adding an external power source (such as hydraulic, electronic or electric motor), thereby significantly reducing the force required for steering. Depending on the power source, the power steering system is mainly divided into a hydraulic power steering system (HPS), an electronic hydraulic power steering system (EHPS) and an electronic power steering system (EPS).
● Hydraulic power steering system (HPS) generates hydraulic oil pressure through a hydraulic pump to assist steering operations. The hydraulic pump is usually driven by the engine, so when the engine is idling, the auxiliary effect of the hydraulic system will be weakened.
● Electronic hydraulic power steering system (EHPS) Adds electronic control to the hydraulic system, generates hydraulic pressure through an electric hydraulic pump, no longer relies on the engine, and improves the flexibility of the system.
● Electronic power steering system (EPS) completely abandons the hydraulic system and relies on electric motors to directly provide steering assistance. This system has the characteristics of fast response speed, light weight and low energy consumption.
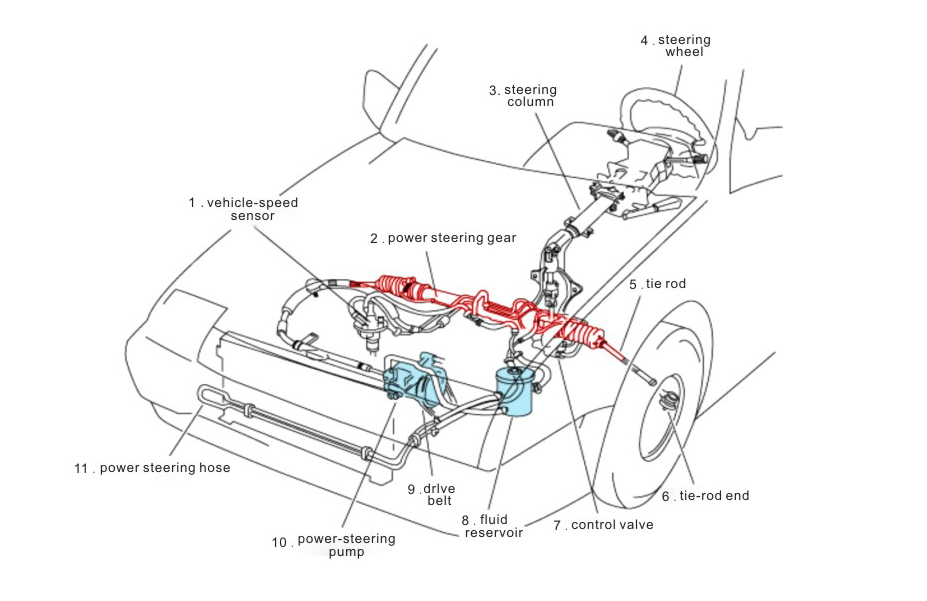
Structure and Working Principle of Manual Steering System and Power Steering System
The working principle and structure of manual steering system and power steering system are significantly different.
1. Structure and principle of manual steering system
The structure of manual steering system is relatively simple, mainly including the following parts:
● Steering wheel: The driver applies turning force through the steering wheel.
● Steering column: Connects the steering wheel and the steering gear, and transmits the rotational motion of the steering wheel to the steering gear.
● Steering gear: Usually a rack and pinion mechanism or a worm gear mechanism, which converts the rotational motion of the steering column into lateral motion and pushes the steering rod.
● Steering rod: Connects the steering gear and the wheel, transmits the lateral motion of the gear to the wheel, and realizes the steering of the wheel.
In this system, the driver's turning force is completely transmitted to the wheel by mechanical means. Therefore, the slower the vehicle speed, the greater the force required for steering. The advantages of the manual steering system are its simple structure, low failure rate, and more direct and precise steering feel at high speeds.
2. Structure and principle of power steering system
The power steering system adds an auxiliary power unit to the manual steering system. Taking the hydraulic power steering system (HPS) as an example, its structure includes:
● Hydraulic pump: usually driven by the engine to generate hydraulic oil pressure.
● Hydraulic oil pipeline: transfer the hydraulic oil generated by the hydraulic pump to the steering rack or steering gear.
● Steering rack or steering gear: reduce the force required for the driver to steer through the pressure of the hydraulic oil.
● Pressure valve and control unit: adjust the hydraulic pressure according to the steering force and speed of the driver to provide appropriate assistance.
In the electronic power steering system (EPS), the hydraulic components are replaced by electric motors. The system uses the electronic control unit (ECU) to accurately control the auxiliary force of the electric motor according to the steering wheel rotation angle and speed, further optimizing the steering sensitivity and comfort.

Operation Experience and Driving Experience of Manual Steering System and Power Steering System
The difference in driving experience between manual steering system and power steering system is particularly obvious. The following is an analysis from three aspects: steering force, control accuracy and driving comfort.
1. Steering force
When the manual steering system is at low speed or parking, the driver needs to apply a large force to turn the steering wheel, especially when driving heavy vehicles or off-road vehicles. However, at high speeds, the steering force of the manual steering system is moderate, and the steering feel is more direct and stable.
The power steering system greatly reduces the driver's steering burden through the assistance of an external power source. Whether it is driving at low speed, reversing or parking in a narrow space, the power steering system can provide easy steering operation. At high speeds, the power steering system usually automatically adjusts the steering force to make the steering wheel feedback more stable, thereby improving control stability.
2. Control accuracy
Since the manual steering system has no power assistance, every subtle steering movement will be directly transmitted to the wheels, so it performs well in control accuracy. Especially on the track or in complex road conditions, the driver can get a clear sense of the road and precise vehicle control through the manual steering system.
Although the power steering system is more comfortable at low speeds and daily driving, it may be slightly inferior in control accuracy. Especially in hydraulic power steering systems, the fluidity of hydraulic oil may cause the steering feel to be slightly vague. However, modern electronic power steering systems have been able to find a balance between comfort and controllability through precise electronic control, providing a good driving experience.
3. Driving comfort
The power steering system is significantly better than the manual steering system in terms of driving comfort. The power steering system can automatically adjust the steering force according to the vehicle speed and driving conditions, so that the driver is not easily fatigued during long-term driving. In addition, the buffering effect of the power steering system can also reduce the intensity of road vibration transmitted to the steering wheel, improving driving comfort.
Since the manual steering system relies entirely on mechanical connections, the steering wheel can directly feel the subtle changes in the road surface. This direct feedback is an advantage in some driving scenarios, but for ordinary drivers, long-term driving may feel tiring.
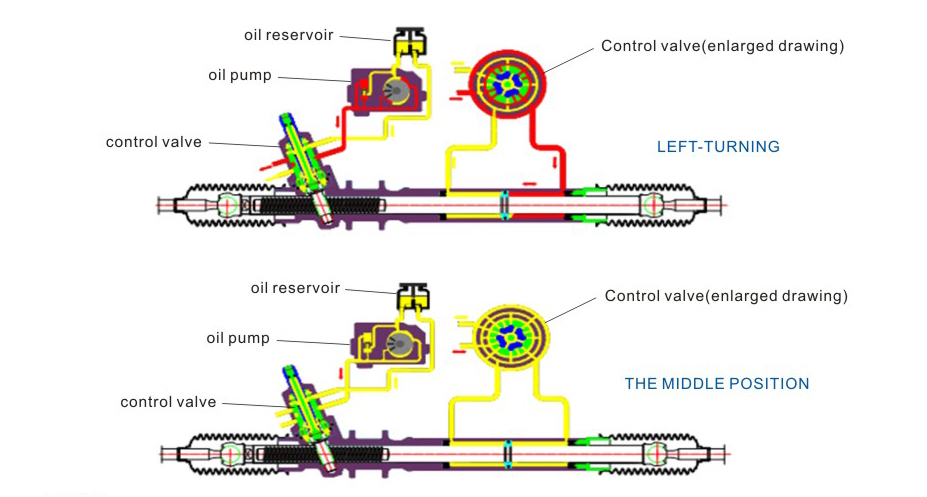
Maintenance and Cost Analysis of Manual Steering System and Power Steering System
In terms of maintenance and cost, there are also significant differences between manual steering system and power steering system.
1. Maintenance and cost of manual steering system
The manual steering system is relatively easy to maintain due to its simple structure. Its main maintenance work includes lubricating the steering gear and checking the wear of the steering rod. Since there are no hydraulic or electronic components, manual steering systems have a lower failure rate and relatively small repair costs.
Manual steering systems generally have a longer lifespan and are more reliable under extreme conditions. For drivers who demand higher vehicle performance, manual steering systems may be more attractive.
2. Maintenance and cost of power steering systems
The maintenance of power steering systems is relatively complex, especially in hydraulic power steering systems. Hydraulic systems require regular inspections of the hydraulic oil level and quality, and timely replacement of hydraulic oil and filter elements to prevent wear and leakage in the system. In addition, aging of components such as hydraulic pumps, oil pipes and valves may also cause system failure and high repair costs.
The maintenance cost of the electronic power steering system (EPS) is relatively low because it has no hydraulic components and does not require replacement of hydraulic oil. However, failures in electronic systems often require professional equipment for diagnosis and repair, and if there is a problem with the electric motor or electronic control unit, the repair cost is also expensive.
Overall, the maintenance cost of power steering systems is higher than that of manual steering systems, especially when the system is aging or fails.

How to Choose a Steering System that Suits Me?
Through an in-depth comparison of the manual steering system and the power steering system in terms of structure, working principle, operating experience, driving experience, maintenance cost, etc., it can be found that the two systems have their own advantages and disadvantages, suitable for different driving needs and preferences.
The manual steering system has a simple structure, low maintenance cost, and high control accuracy, which is suitable for drivers who pursue driving pleasure and have high requirements for vehicle control. The power steering system provides a more comfortable driving experience, especially in low-speed driving and daily driving, which is more relaxed and suitable for most daily car needs.
For car owners, the choice of steering system should be determined according to personal driving habits, vehicle usage scenarios, and requirements for vehicle performance. No matter which system is chosen, regular maintenance and inspection are the key to ensure the normal operation of the steering system. Only on the basis of a full understanding of the two systems can the most appropriate choice be made to improve the driving experience and the overall performance of the vehicle.




