What is the biggest safety risk in repairing a hydraulic power rack?
Hydraulic power steering systems, especially hydraulic power racks, play a vital role in modern cars. Hydraulic power racks provide precise and easy steering experience for the steering wheel through a hydraulic power system, and are standard in many traditional cars. However, due to the complexity of its working principle and the operation closely related to the hydraulic system, repairing hydraulic power racks may bring some potential safety risks. These risks not only involve the safety of the system itself, but also the technical challenges and hidden problems that may be encountered during the repair process.
This article will comprehensively analyze the safety risks that hydraulic power racks may bring during the repair process, discuss in detail the sources of these risks, and how to effectively reduce and avoid these risks to ensure that the repair work of hydraulic power racks can proceed smoothly while ensuring the driving safety of the vehicle.

What is the principle of hydraulic power racks?
The hydraulic power rack system is usually composed of multiple components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic oil pipelines, hydraulic boosters and steering racks. Its working principle is to pressurize the hydraulic oil through a hydraulic pump and send it to the hydraulic booster. The hydraulic booster converts the inflowing hydraulic oil into mechanical energy to help the driver turn the steering wheel. The hydraulic power rack transmits this mechanical energy to the wheels through the movement of the rack and pinion, achieving an effective connection between the steering wheel and the wheels.
The design of the hydraulic power rack allows the vehicle to provide more power at low speeds and automatically reduce the power at high speeds to ensure driving accuracy and stability. The advantage of the hydraulic power steering system is that it can provide relatively large power output, especially on large vehicles or vehicles that require greater steering force.
What are the safety risks in the repair of hydraulic power racks?
The safety risks in the repair of hydraulic power racks are:
1. The risk of high-pressure hydraulic oil leakage
2. Pressure instability caused by hydraulic pump or pipeline failure
3. Hydraulic oil contamination caused by incorrect operation
4. Misinstallation or mismatch of steering rack and hydraulic power assist components
5. Damage caused by overload of hydraulic system

1. Risk of high-pressure hydraulic oil leakage
The hydraulic power steering system relies on hydraulic oil to provide power, and these hydraulic oils maintain extremely high pressure in the system. The working pressure in the hydraulic power rack is usually between 1000 PSI and 1500 PSI, which is much higher than the pressure of ordinary household water pipes. Leakage of hydraulic oil, especially when the seals of high-pressure pipelines or hydraulic cylinders are damaged, may cause a series of safety problems.
The safety risks brought by hydraulic oil leakage may not only cause system failure, but also cause more serious accidents such as fire. Hydraulic oil itself is flammable. Once it leaks and contacts high-temperature surfaces or fire sources, it may cause fires, posing a great threat to vehicle owners and maintenance personnel. In addition, hydraulic oil leakage will cause the steering system to fail, causing the driver to lose the ability to control the vehicle, increasing the risk of accidents.
2. Pressure instability caused by hydraulic pump or pipeline failure
The pump in the hydraulic system is the heart of the system. It is responsible for pressurizing the hydraulic oil and providing power assistance. If the hydraulic pump fails or the pipeline is damaged, it may cause unstable hydraulic pressure. This will not only make the output of the hydraulic power rack uneven, but may also cause a sudden loss of steering force or even a complete loss of steering ability.
Failure of the hydraulic pump or pipeline is often manifested as heavy steering or vibration of the steering wheel, and in severe cases, it may cause the steering wheel to lose any power assistance. Such problems usually do not immediately cause the vehicle to lose control, but when driving fast or making emergency turns, the failure to quickly restore normal steering power assistance may cause traffic accidents. Failure to promptly detect or resolve hydraulic pump and pipeline problems during maintenance may result in serious driving risks.
3. Hydraulic oil contamination due to incorrect operation
Hydraulic system maintenance involves operations such as replacement, cleaning, and filtering of hydraulic oil. Hydraulic oil contamination usually comes from external particles, worn metal chips, aged rubber seals, etc. If improper operation is performed during maintenance, contaminants may be introduced into the hydraulic system, resulting in hydraulic oil contamination.
Contaminated hydraulic oil not only affects the normal operation of the hydraulic system, but may also cause excessive wear of components such as hydraulic pumps and hydraulic cylinders, accelerating system aging. Hydraulic oil contamination may cause unstable internal system pressure, increase the risk of hydraulic system failure, and ultimately lead to loss of vehicle steering ability. Failure to strictly clean the working environment, tools, and replace the appropriate hydraulic oil during maintenance will increase the possibility of system failure and bring potential safety hazards to the owner.
4. Misinstallation or mismatch of steering rack and hydraulic power assist components
The maintenance process of the hydraulic power rack involves the removal and reinstallation of many key components. The incorrect installation of any component or the replacement of non-compliant components may cause abnormal operation of the steering system. For example, the mismatch of components such as steering racks, hydraulic boosters, and seals may result in the inability to stably supply pressure in the hydraulic system, which in turn affects the normal operation of the entire steering system.
During the maintenance process, if the installation position, installation angle, or sealing performance of the steering rack and related components is not given enough attention, problems such as system loosening, oil seal failure, and hydraulic oil leakage may occur, resulting in the loss of steering function. Since the hydraulic system involves a high-pressure working environment, these improper installation situations may aggravate the consequences of the failure and even pose a threat to the safety of maintenance personnel and drivers.
5. Damage caused by overload of the hydraulic system
The hydraulic power rack and the entire hydraulic steering system must operate within the set working range. Excessive load will cause overload of the hydraulic system. When the hydraulic system is overloaded, the hydraulic pump, hydraulic cylinder, and other components may be damaged due to excessive pressure. Common causes of overload include excessive operation of the steering system, excessive hydraulic oil pressure, or long-term operation under extreme conditions.
If the system load abnormality is not discovered in time during maintenance, or if necessary inspections and adjustments are not made, the system may be in a dangerous working state. An overloaded hydraulic system is not only prone to damage to components such as the hydraulic power rack, but may also cause steering failure and increase safety risks during driving.
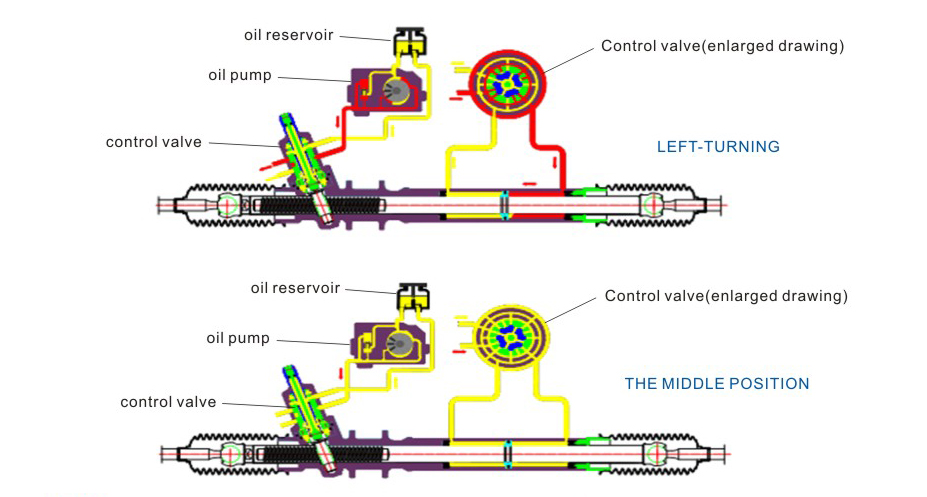
What are the safety precautions in the maintenance of hydraulic power racks?
The safety precautions in the maintenance of hydraulic power racks are:
1. Strictly control the pressure of the hydraulic oil
2. Use professional equipment and tools
3. Regularly check seals and connecting pipes
4. Ensure the cleanliness and quality of the hydraulic oil
5. Train and standardize operating procedures
1. Strictly control the pressure of the hydraulic oil
The maintenance of the hydraulic power rack first requires strict control of the pressure of the hydraulic oil. Maintenance personnel need to understand the working pressure of the system before operation, and use appropriate pressure testing tools during operation to ensure that the hydraulic system is within the normal pressure range. When performing maintenance, be sure to follow the pressure release procedure of the hydraulic oil system to avoid accidents caused by high-pressure oil leakage.
2. Use professional equipment and tools
The maintenance of the hydraulic system requires professional equipment and tools, such as hydraulic pressure gauges, oil pump testers, etc. These tools can help maintenance personnel accurately measure the flow and pressure of hydraulic oil to ensure the normal operation of the system. When replacing hydraulic oil and disassembling hydraulic power racks, ensure that all tools and equipment are in good condition to avoid secondary damage caused by improper tools.
3. Regularly check seals and connecting pipes
The maintenance of hydraulic power racks is not only about replacing damaged parts, but also about checking seals and connecting pipes. Aging and damage of seals are common causes of hydraulic oil leakage. If the connecting pipes are loose or damaged, it may cause unstable system pressure. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the inspection and replacement of these parts during maintenance to ensure the sealing of the hydraulic system.
4. Ensure the cleanliness and quality of hydraulic oil
In the maintenance of hydraulic power racks, the replacement of hydraulic oil is a crucial step. In order to avoid contamination, maintenance personnel should ensure the cleanliness of the working environment and use special oil filters and filters to ensure the cleanliness of the new oil. In addition, the appropriate hydraulic oil should be selected according to the requirements of the vehicle manufacturer, and it should be replaced strictly in accordance with the prescribed replacement cycle and operating specifications.
5. Training and standardized operation procedures
The maintenance of hydraulic power racks requires professional technicians to operate, so the training of maintenance personnel is particularly important. Maintenance personnel need to understand the working principle of the hydraulic system, common faults and repair methods, and master safe operation specifications. In addition, maintenance techniques and safety standards should be updated regularly to ensure safety during operation.
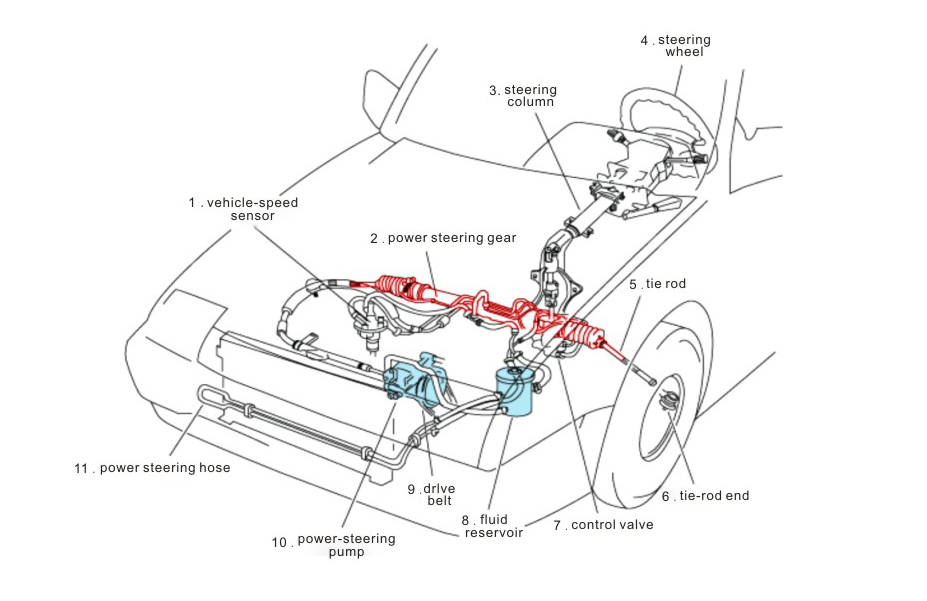
DKM Company has been a leader in automotive steering manufacturing for over two decades, producing high-quality products for domestic and international clients. Our factory employs over 500 skilled workers and 280+ machines to manufacture 300,000 units annually. With cost-effective options for wholesale buyers, we cater to distributors across Europe, Southeast Asia, and North America. Request a quote today for customized steering systems, factory-direct pricing, and exclusive bulk order promotions!




